Recent Posts
-
How to Reduce Wireless Microphone Background Noise
Wireless microphones are a popular choice for a variety of events, from speeches and church services to performances and presentations. However, background noise can often be a major issue. If you're struggling with unwanted noise, here are some effective tips to help you reduce wireless microphone background noise and improve your audio quality.
03/01/2025
-
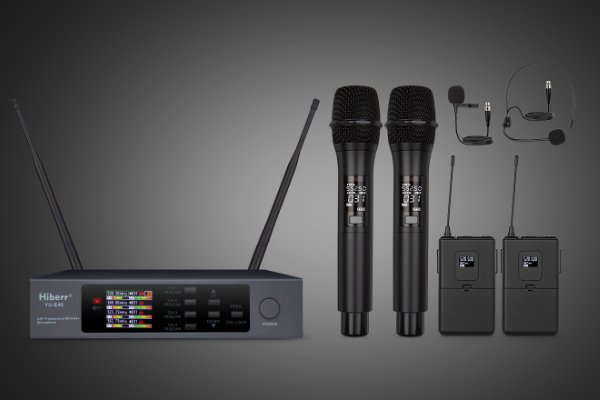
Hiberr Microphones: Leading the Charge in Modern Audio Solutions
Microphones are more than just tools—they're instruments of communication, creativity, and collaboration. Hiberr, with its innovative designs and commitment to quality, is poised to redefine the audio landscape for the digital age.
10/08/2023
-
Understanding the Evolution and Importance of the Wireless Microphone
Understanding the Evolution and Importance of the Wireless Microphone in Modern Times
10/06/2023
-
Understanding Microphone Differences: Hosts vs. Singers
When choosing a microphone, understanding its primary use is essential. The difference between microphones tailored for hosts and those for singers is quite stark.
09/28/2023
-
What affects the receiving distance of uhf wireless microphone? How to solve?
Long-distance wireless microphone systems are pivotal in various events and settings. Their performance, however, can be affected by a myriad of factors. Understanding and addressing these factors can optimize your microphone's receiving distance. Here's a breakdown:
09/23/2023
-
What is the signal-to-noise ratio of a microphone?
The Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of a microphone measures the ratio between the desired audio signal and the undesired background noise inherent in the microphone. Essentially, it quantifies how much clearer the desired sound is compared to the background noise. It's typically expressed in decibels (dB). In the context of microphones, SNR often refers to the difference between the microphone's sensitivity and its self-noise or equivalent noise level.
09/22/2023
What is the signal-to-noise ratio of a microphone?
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a microphone measures the ratio between the desired audio signal and the undesired background noise inherent in the microphone. Essentially, it quantifies how much clearer the desired sound is compared to the background noise. It's typically expressed in decibels (dB). In the context of microphones, SNR often refers to the difference between the microphone's sensitivity and its self-noise or equivalent noise level.
For microphones, a higher SNR is usually more desirable as it indicates that the microphone can capture a clearer audio signal relative to its inherent noise.
Typical SNR Values for Microphones:
Studio Condenser Microphones: These are often used in controlled recording environments. They can have very high SNRs, commonly ranging from 70 dB to 85 dB or more. Some of the best studio microphones might even exceed 90 dB.
Dynamic Microphones: Commonly used for live sound applications, these mics generally have a lower SNR than studio condenser microphones. SNRs might range from 55 dB to 70 dB, depending on the quality and design.
Field Recording Microphones: Used for capturing sounds in outdoor or unpredictable environments, the SNR for these microphones can vary widely based on design and intended use, but good ones might fall in the range of 60 dB to 80 dB.
Regarding the SNR of performance-level wireless microphones:
The exact SNR of a wireless microphone can vary based on its design, quality, and the technology used. However, for professional or performance-level wireless microphones, it's common to see SNR values ranging from 90 dB to 120 dB. Generally, a higher SNR is preferred, as it would produce clearer audio with less background noise.