Recent Posts
-
How to Reduce Wireless Microphone Background Noise
Wireless microphones are a popular choice for a variety of events, from speeches and church services to performances and presentations. However, background noise can often be a major issue. If you're struggling with unwanted noise, here are some effective tips to help you reduce wireless microphone background noise and improve your audio quality.
03/01/2025
-
Hiberr Microphones: Leading the Charge in Modern Audio Solutions
Microphones are more than just tools—they're instruments of communication, creativity, and collaboration. Hiberr, with its innovative designs and commitment to quality, is poised to redefine the audio landscape for the digital age.
10/08/2023
-
Understanding the Evolution and Importance of the Wireless Microphone
Understanding the Evolution and Importance of the Wireless Microphone in Modern Times
10/06/2023
-
Understanding Microphone Differences: Hosts vs. Singers
When choosing a microphone, understanding its primary use is essential. The difference between microphones tailored for hosts and those for singers is quite stark.
09/28/2023
-
What affects the receiving distance of uhf wireless microphone? How to solve?
Long-distance wireless microphone systems are pivotal in various events and settings. Their performance, however, can be affected by a myriad of factors. Understanding and addressing these factors can optimize your microphone's receiving distance. Here's a breakdown:
09/23/2023
-
What is the signal-to-noise ratio of a microphone?
The Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of a microphone measures the ratio between the desired audio signal and the undesired background noise inherent in the microphone. Essentially, it quantifies how much clearer the desired sound is compared to the background noise. It's typically expressed in decibels (dB). In the context of microphones, SNR often refers to the difference between the microphone's sensitivity and its self-noise or equivalent noise level.
09/22/2023
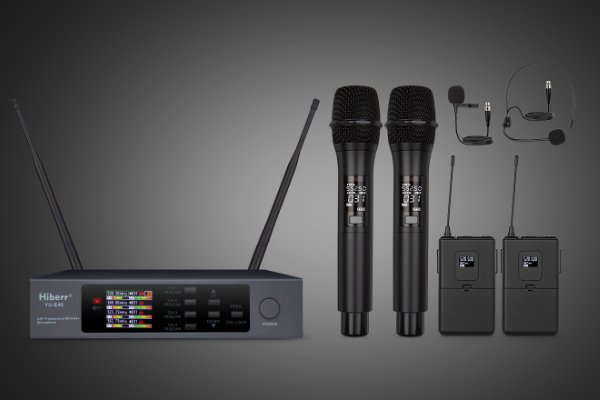
A Comprehensive Guide to Evaluating Wireless Microphone Quality: Key Parameters You Should Know
When evaluating wireless microphones, especially from an audio equipment engineering perspective, there are several indicators and parameters that need to be considered to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and user satisfaction. Here are some important indicators and parameters to consider:
1. Frequency Range and Response: This indicates the range of audio frequencies the microphone can pick up. Ideally, a wireless microphone should have a frequency response that captures the entire human voice range (roughly 80Hz to 18kHz) and beyond, depending on the application.
2. Transmission Range: This indicates how far the microphone can be from the receiver and still maintain a reliable connection. For most events, a range of at least 100 meters is preferred.
3. RF (Radio Frequency) Stability: This assesses how immune the system is to interference and dropouts. Consider factors like frequency agility and diversity reception.
Typical Value: Varies based on regulation but common bands include UHF (470 MHz to 900 MHz) and 2.4 GHz.
4. Dynamic Range: This measures the difference between the softest and loudest sounds the microphone can capture without distortion. A larger dynamic range indicates better performance.
Typical Value: 85 dB to 110 dB.
5. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): A higher SNR means that the microphone produces a cleaner sound with less background noise.
Typical Value: Higher than 95 dB for a quality microphone.
6. Total Harmonic Distortion (THD): Ideally, this should be as low as possible. It measures how much the signal is distorted when compared to the original source.
Parameter: Measure of non-linearities in the audio signal pathway.
Typical Value: Below 0.5% for quality systems.
7. Battery Life: As these are wireless devices, their operating time on a single charge or set of batteries is crucial for uninterrupted performance.
Typical Value: 10 Hours
8. Latency: This refers to the time delay between the sound being captured by the microphone and it being output from the receiver. For live performances, lower latency is essential.
Typical Value: Less than 20 ms
9. Form Factor and Build Quality: Depending on the intended use (lavalier, handheld, headset, etc.), the physical design and durability of the microphone and transmitter are crucial.
10. Connectivity Options: Examine what types of outputs the receiver offers (XLR, 1/4" jack, etc.) and whether it provides features like phantom power for condenser mics.
11. Number of Channels: If you're setting up multiple microphones in one location, having multiple channels that can operate simultaneously without interference is critical.
12. Automatic Frequency Scanning: Some advanced wireless microphone systems can automatically scan and select the best frequency to avoid interference.